Bone Extracellular Matrix Is Composed of Which of the Following
The core matrisome 3 comprises approximately 300 proteins. Mature bone cells osteoblasts.

The Extracellular Matrix Composition The Brain Extracellular Matrix Download Scientific Diagram
Bone matrix is a composite material that derives its strength from a compression-resistant mineral phase and a tension-resistant network of collagen fibers.

. Bone tissue ECM consists of collagen elastic and reticular fibers. Bone matrix also known as osteoid consists of about 33 organic matter mostly Type I collagen and 67 inorganic matter calcium phosphate mostly hydroxyapatite crystals. Exocytosis Near the center of the cartilage model future diaphysis periosteal capillaries grow into the disintegrating calcified cartilage and induce the growth of the.
Collagen Fibers very flexible but resist stretching b. Maintain the bone Major Components of Extracellular Matrix. The following sequence represents part of the primary structure of collagen.
Bone tissue ECM consists of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals and collagen fibers. In many cases these materials are designed to mimic the biochemistry andor structure of native bone extracellular matrix ECM. Major components include collagens proteoglycans elastin and cell-binding glycoproteins each with distinct physical and biochemical properties.
Degraded bone proteins and extracellular matrix minerals leave the side of an osteoclast opposite the ruffled border by _____ and enter the interstitial fluid. The extracellular matrix of bone tissue is largely composed of collagen and inorganic salts. With the exception of phospholipids and keratin the extracellular matrix surrounding your cells contains a proteoglycans b collagen and c reticular fibers.
Schaefer and Schaefer 2010. Mature bone matrix is composed of _____ material like collagen and proteoglycans and _____ material like hydroxyapatite. The ECM is composed of two main classes of macromolecules.
Reticular Fibers very fine short collagen fibers that branch to form a supporting network c. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages the composition of ECM varies between. A proteoglycan is composed of a protein core surrounded by long chains of starch-like molecules called glycosaminoglycans.
6 Wh ich of the following best characterizes the extracellular matrix ECM of bone tissue. Bone tissue ECM consists of only calcium hydroxyapatite crystals. There are collagen fibres mostly type I 90 with some type V.
6 Which of the following best characterizes the extracellular matrix ECM of bone tisue. Which component of the extracellular matrix of an animal cell can communicate through the hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments of the cell. Match the following connective tissue component with its description.
Proteoglycans PGs and fibrous proteins see Boxes 1 and 2 Jarvelainen et al 2009. The main fibrous ECM proteins are collagens elastins fibronectins and laminins see panel 1 of the poster Alberts et al 2007. Large bone breakdown cells derived from the fusion if as many as 50 monocytes type of WBC and are concentrated in the endosteum.
Components of the extracellular matrix. Elastic Fibers have the ability to return to their original shape after being stretched 2. Extracellular matrix which is made up of an organic matrix 30 containing proteoglycans but less than cartilage glycosaminoglycans glycoproteins osteonectin anchors bone mineral to collagen and osteocalcin calcium binding protein.
Imbibes and retains water is reinforced with fibrous proteins usually composed of a combination of hyaluronic acid and proteoglycans. The extracellular matrix is made up of proteoglycans water minerals and fibrous proteins. The extracellular matrix of connective tissue is composed of ground substance and fibers.
Extracellular matrix a Bone-producing cell b Liquid portion of blood c Cartilage-producing cell d Type of fibroblast e Nonliving material located between the cells of a connective tissue. Answer parts a b and c below. Collagen is composed of 3 polypeptide α chains that form a triple helical structure.
Collagen gives the bone. Bone tissue consists of extracellular bone _____ and bone cells. The principal fiber type is collagen the most abundant protein in the body with elastic fibers as a minor element.
In ordinary connective tissue the ground substance consists mainly of water. In biology the extracellular matrix is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals such as collagen enzymes glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Fibrous protein hydrated gel multiadhesive matrix protein cells.
Bones mineral phase calcium hydroxyapatite Ca 10 PO 4 6 OH 2 is subdivided into a mosaic of tiny microcrystallites thereby creating a large surface area for ion exchange and limiting the spread. The natural ECM within bone has a well-defined organization consisting of oriented collagen I fibers with intervening nanocrystals of carbonated hydroxyapatite HA a type of calcium phosphate CaP mineral. Two main classes of extracellular macromolecules make up the matrix.
1 polysaccharide chains of the class called glycosaminoglycans GAGs which are usually found covalently linked to protein in the form of proteoglycans and 2 fibrous proteins including collagen elastin fibronectin and laminin which have. Keratin is a protein composed of intermediate filaments that is found in hair and skin. The main cells in bone tissue and maintain its daily metabolism such as the exchange of nutrients and wastes with the blood.
Bone tissue ECM consists of only calcium hydroxyapatite crystals. Collagen I which comprises. Bone tissue ECM consists of only collagen fibers.
Which of the following describes the zone of cell hypertrophy in an epiphyseal plate. Collagen a strong fibrous protein found in connective tissue bone and the extracellular matrix has a structure in which three helices wind around each other to form a triple helix. Phospholipids are the lipids that compose the plasma membrane.

Extracellular Matrix Ecm And Cellular Components Of Tendons Modified Download Scientific Diagram

The Extracellular Matrix Of The Osteosarcoma Niche Modelled In 3d Download Scientific Diagram

Histology Of Bone Basic Anatomy And Physiology Red Bone Marrow Plasma Membrane

Extracellular Matrix Of Cartilage Three Classes Of Proteins Exist In Download Scientific Diagram
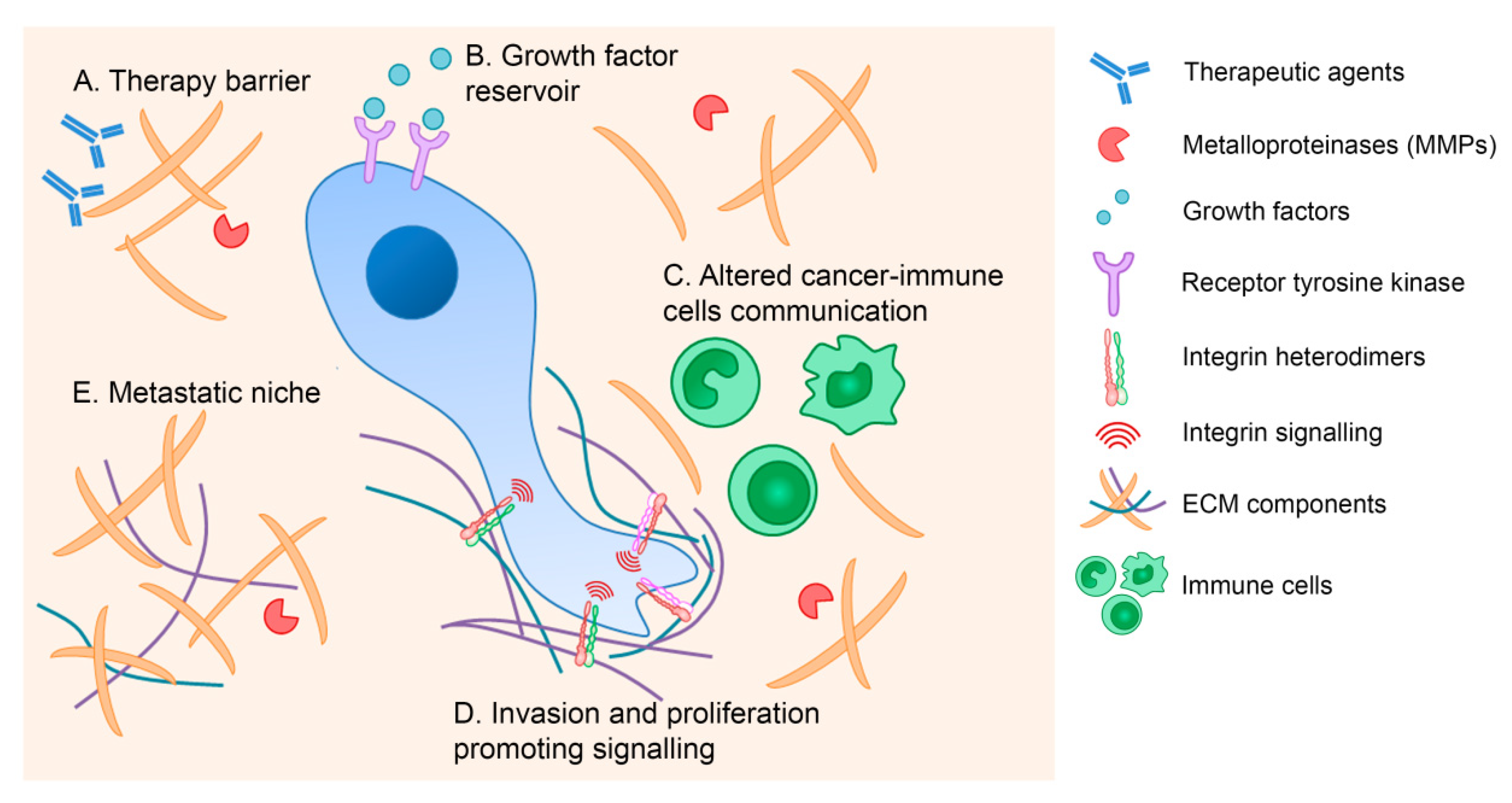
Cells Free Full Text The Extracellular Matrix An Accomplice In Gastric Cancer Development And Progression Html
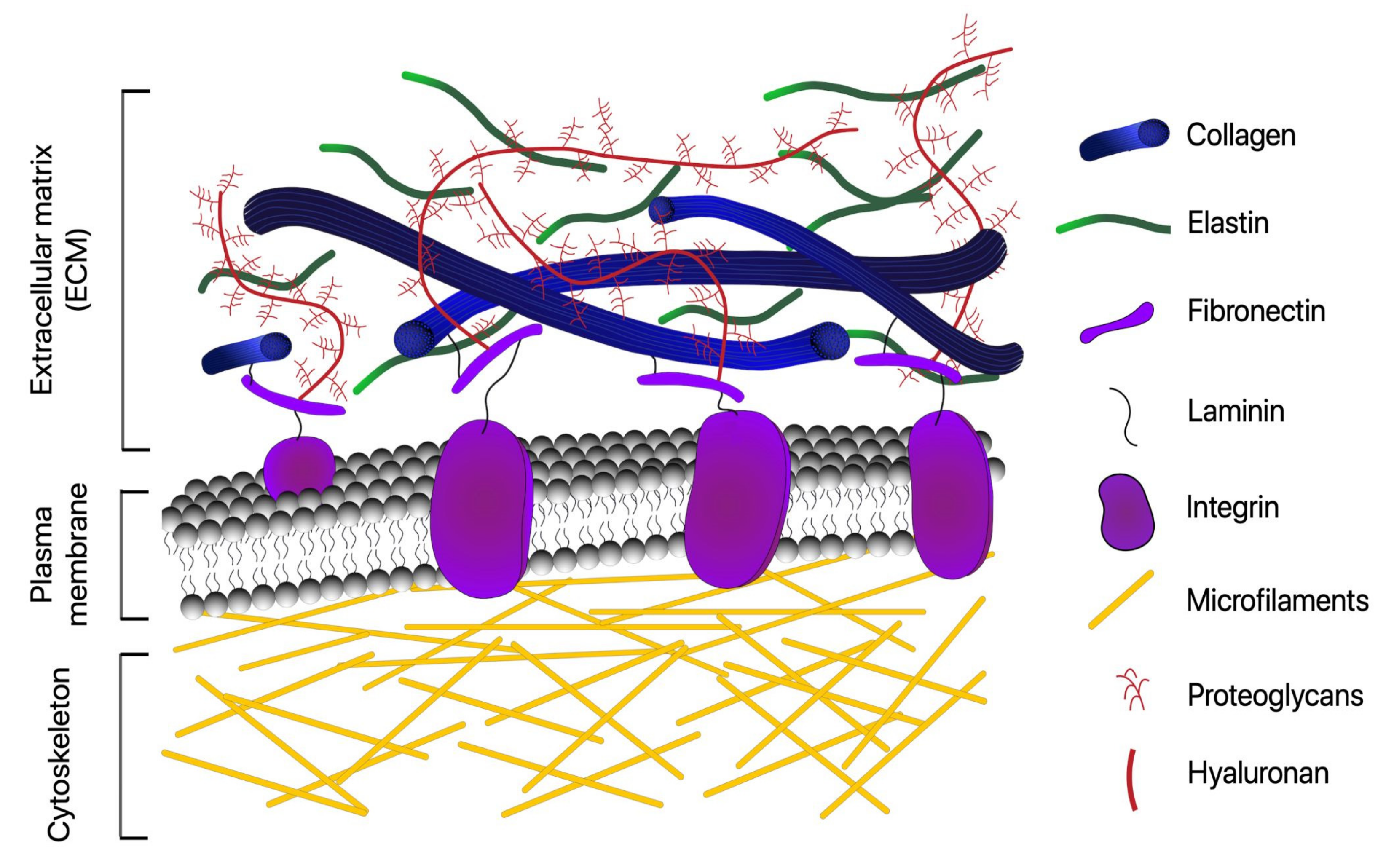
Cells Free Full Text Optical Microscopy And The Extracellular Matrix Structure A Review Html
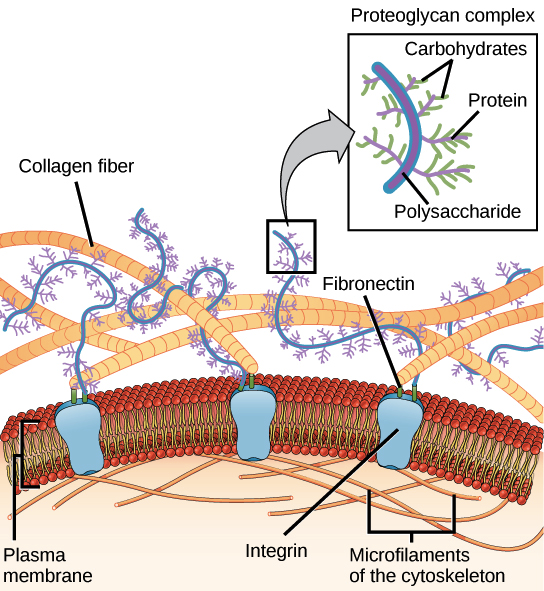
The Extracellular Matrix And Cell Wall Article Khan Academy
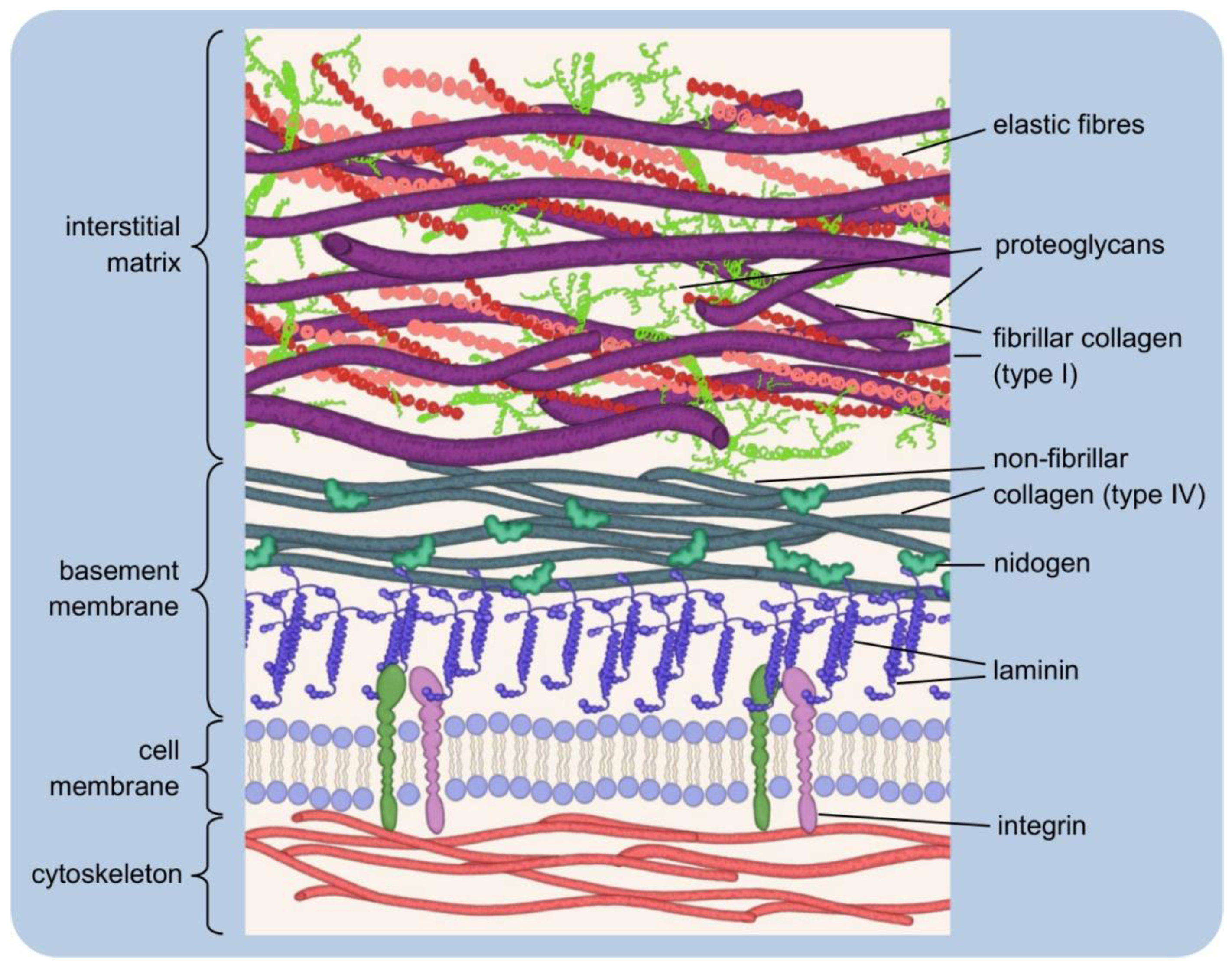
Cells Free Full Text Into The Tissues Extracellular Matrix And Its Artificial Substitutes Cell Signalling Mechanisms Html

The Extracellular Matrix Composition The Brain Extracellular Matrix Download Scientific Diagram

Extracellular Matrix Of Cartilage Three Classes Of Proteins Exist In Download Scientific Diagram

Extracellular Matrix Structure Sciencedirect

Schematic Structure Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm In The Brain The Ecm Download Scientific Diagram

Extracellular Matrix Apbiology Tissue Biology Body Tissues Anatomy And Physiology

The Extracellular Matrix Of The Osteosarcoma Niche Modelled In 3d Download Scientific Diagram

Collagen Of Extracellular Matrix And Its Biology In Invertebrates The Download Scientific Diagram

Chapter 10 Cell And Tissue Architecture Cytoskeleton Cell Junctions And Extracellular Matrix Cell Junction Cells And Tissues Eukaryotic Cell
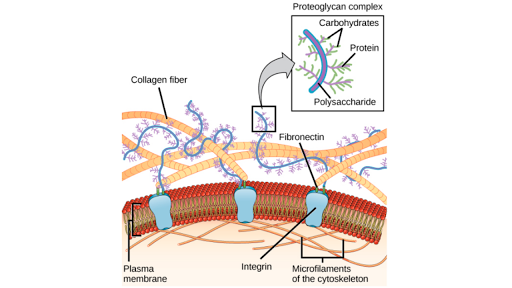
The Extracellular Matrix And Cell Wall Article Khan Academy

Extracellular Matrix Ecm Compartments Schematic Representation Of Download Scientific Diagram

Example Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm Implications The Extracellular Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment